Extraction of Cast Iron from Ore
Introduction: Iron is a very useful metal. About 4.15% by weight of the earth’s crust is iron. Iron occurs as ore in earth. Some important ores are magnetite (Fe3O4), Hematite (Fe2O3), Limonite (Fe2O3.3H2O), Iron Pyrites (FeS2). Generally, we use cast iron. This iron can be extracted from the ore by ‘Carbon Reduction Method’. There are four steps for cast iron extraction which are
(i)Crushing The Ore
(ii)Condensation of Ore
(iii) Conversion of Condensed Ore into Oxide (i)Calcination & (ii)Roasting
(iv) Conversion of Metallic Oxide into Free Metal
(a)Crushing The Ore: Joe crusher Ball crusher
Firstly, the stones of ore are crushed in the Joe crusher to smaller pieces and then they are turned into powder or small lattices in the Ball crusher.
(b)Condensation of Ore
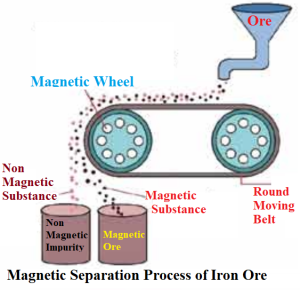
The crushed powder of Iron ores still contains the impurities mixed with them. The process that is employed to separate these impurities from the intended metals is called condensation of ores. Magnetic separation is one the condensation method for iron extraction as its ore has magnetic property.
Magnetic Separation Method
The Crushed ores are passed through a plastic conveyor belt. The outer wheel of the conveyor belt has the magnetic property. It attracts the magnetic ores or gangue and they are gathered below and near the wheel. The nonmagnetic portion of the mix gathers separately a little afar. As a result, the ore is separated from the gangue.
(c) Conversion of Condensed Ore into Oxide (i)Calcination & (ii)Roasting
The condensed ore of iron can be converted into iron oxide by (i)Calcination or (ii)Roasting
In calcination process, the iron ores are heated at a lower temperature than melting point in absence of air. Then organic impurities and moisture are removed. In this process, limonite ore, Fe2O3.3H2O and FeCO3 are converted into iron oxide.
Fe2O3.3H2O Fe2O3 + 3H2O
FeCO3 FeO + CO2
In roasting process, pyrites ore is heated at a lower temperature than melting point in presence of air. Here, Iron pyrite is converted into iron oxide.
2FeS2 + 3O2 = 2FeO + 4SO2
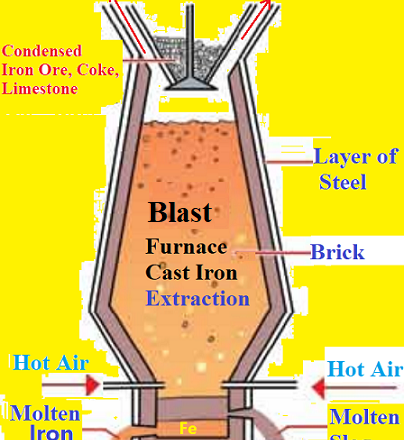
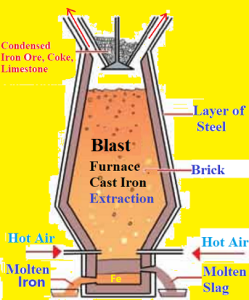
(d) Conversion of Metallic Oxide into Free Metal: Smelting
The metallic oxides (Iron oxides) obtained from roasting and calcination process need to reduction to convert into metal in Blast Furnace. The ‘Carbon Reduction Method’ is used for iron extraction. Blast Furnace It is a tall cylindrical furnacen made of steel. It is lined inside with fire bricks. It is narrow at the top and has an arrangement for the introduction of ore and outlet for waste gases. The concentrated ore is mixed with calculated quantity of coke, limestone and the mixture is put in the Blast Furnace from top. In the same time, hot air is entered into the bottom of the furnace, tuyere. This process is called smelting.
Chemical Reactions in Blast Furnace:
(i)Formation of Carbon Monoxide: Near the bottom of the furnace, coke burns in air to form Carbon Dioxide and a lot of heat is produced. We get a temperature of about 1875 K. This CO2 further reacts with more coke and is reduced to CO.
C + O2 = CO2 ; C + CO2 = CO
(ii) Reduction of Iron oxides into Iron: In the upper part of the furnace, it is Stock column part, the temperature is between 4000C to 7500C, Here, Iron oxides are reduced to Iron by CO. This molten Iron is collected at the bottom of the furnace.
Fe2O3 + CO ® Fe3O4 + CO2 [At 4000C temperature ]
Fe3O4 + CO ® FeO + CO2 [At 6000 C temperature ]
FeO + CO ® Fe + CO2 [At 7500 C temperature ]
(iii)Reaction in the middle part, Bosh area of the furnace:
The lime stone is decomposed into lime, CaO and carbon dioxide at 900-10000C temperature in the middle of furnace. Here, This CaO reacts with silica (sand) present in the ore to form calcium silicate, slag(CaSiO3).
CaCO3 ® CaO + CO2 [At 10000C temperature]
CaO + SiO2 ® CaSiO3
Slag is lighter than molten iron so it floats over molten iron and protects it from oxidizing back into its oxides.
(iv)Reaction in the hearth area of the Furnace:
In this part of the furnace, the temperature is about 1300-15000C. The mineral impurities contain calcium phosphate, manganese dioxide, silica etc. Calcium phosphate is decomposed to calcium oxide and phosphorous pentoxide by heat. Phosphorous pentoxide, manganese oxide, manganese dioxide and silica produce phosphorous, manganese, silicon respectively by reduction with red heated coke.
Ca3(PO4)2=3CaO + P2O5
P2O5 +5C=2P+ 5CO
Mn2O3 +3C = 2Mn + 3CO
MnO2 + 2C = Mn + 2CO
SiO2 + 2C = Si + 2CO
At 13000C temperature, Iron is melted into liquid. Molten iron and slag are assembled two different layer in the bottom of the furnace. Solid iron known as pig iron or cast iron is obtained by cooling the collected molten iron from the bottom of furnace. Cast Iron (or Pig Iron) contains 4-5% Carbon along with traces of other impurities like Silicon, Phosphorus, Manganese, Sulfur etc.